Understanding Ethereum Transactions: « No Entry » and Mining Generated Coins
As a cryptocurrency enthusiast, it is not uncommon to come across unusual transactions on blockchain platforms. I recently came across a notable example of a transaction labeled « Newly Generated Coins » on Blockchain.info, which piqued my curiosity about their implications. In this article, we will dig deeper into what these labels mean and explore the relationship between mined coins and the « No Entry » label.
Blockchain.info: Cryptocurrency Portal
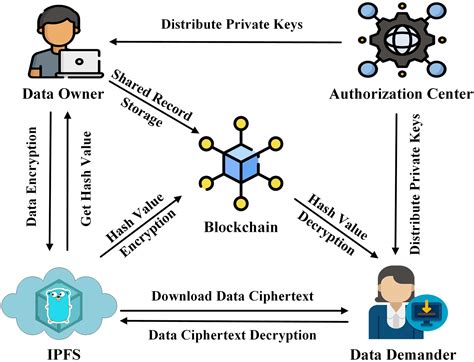
Blockchain.info is one of the most popular cryptocurrency exchanges and trackers available on the internet. It provides detailed information about individual transactions in the blockchain network, including transaction hashes, block heights, and timestamps. By viewing this data, users can obtain information about Ethereum transactions that are used for various purposes on the blockchain.
Transaction label « No entry »
When we come across a transaction marked as « Newly Generated Coins », it may seem counterintuitive at first glance. However, in the context of Ethereum, this tag usually indicates that a transaction involves coins or tokens generated by mining. Here’s what’s behind this label:
- Mining Activity: Over the past few years, the Ethereum network has seen a significant increase in mining activity. Miners compete to confirm transactions and create new blocks, which incentivizes their efforts through rewards. This process is known as « mining ».
- New Coin Creation: As part of the mining process, new coins are created using a complex algorithm called Ethash (SHA-256). These newly generated coins are then added to the Ethereum ecosystem, either through mining or stored in existing addresses.
- Transaction Mark: A « No Entry » mark suggests that this transaction does not require any input from the sender’s wallet (i.e., no payment is required to initiate the transaction). Instead, it involves the creation of new coins through mining.
30 Confirmations and High Transaction Volume
The fact that this transaction has 30 confirmations on Blockchain.info is often used as a metric to assess its legitimacy. In the context of Ethereum, higher confirmation numbers typically indicate more confidence in the validity of the transaction. With 30 confirmations, it suggests that the sender’s wallet was involved in the transaction process and that coins were successfully transferred from one address to another.
However, having 30 confirmations does not necessarily mean that all of these transactions are authentic or valid. It is possible for an account with high transaction volume to accumulate more transactions with « Forbidden Entry » marks without any malicious activity.
Mined Coins: A Double-Edged Sword
The existence of mined coins on the Ethereum blockchain has both positive and negative implications:
- Increased Security
: By introducing new coins through mining, the network becomes more secure as it adds a layer of randomness to transactions.
- Reducing dependence on central authorities: The decentralized nature of the Ethereum blockchain encourages users to trust each other without relying on centralized institutions.
However, the existence of mined coins also raises concerns about:
- Centralization and Censorship: If too many accounts are involved in the creation of new coins, this can lead to increased centralization and possible censorship.
- Regulatory Oversight: As more transactions involving new coins come into play, regulatory bodies may scrutinize these activities, which could impact the ecosystem.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a « No input » transaction tag on the Ethereum blockchain indicates that the transaction involves coins generated by mining.

Laisser un commentaire